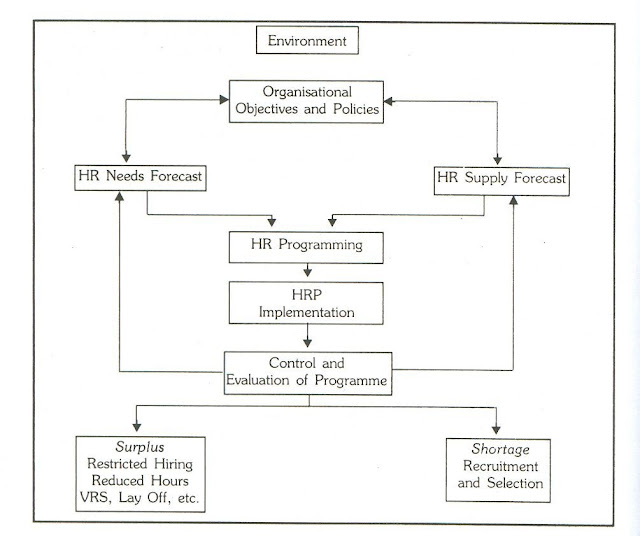
Human Resource Planning Process
Figure 2.2: The HRP Process
Environmental
Scanning:
It refers to the systematic monitoring of the external forces
influencing the organization. The following forces are essential for pertinent
HRP.
• Economic
factors, including general and regional conditions.
• Technological
changes
• Demographic
changes including age, composition, literacy,
Political and legislative issues, including laws and administrative rulings
• Social
concerns, including child care, educational facilities, and priorities.
By scanning the environment for changes that will affect an
organization, managers can anticipate their impact and make adjustments early.
Organizational
Objectives and Policies: The HR plan is usually derived from the organizational
objectives. Specific requirements in terms of the number and characteristics of
employees should be derived from organizational objectives
Once the organizational objectives are specified,
communicated, and understood by all concerned, the HR department must specify
its objective regarding HR utilization in the organization.
HR Demand
Forecast:
Demand forecasting is the process of estimating the future
quantity and quality of people required to meet the future needs of the
organization. Annual budget and long-term corporate plan when translated into
activity form the basis for HR forecast.
For eg: in the case of a manufacturing company, the sales
budget will form the basis for the production plan giving the number and type of
products to be produced in each period. This will form the basis upon which the
organization will decide the number of hours to be worked by each skilled
category of workers. Once the number of hours required is the available organization
can determine the quality and quantity of personnel required for the task.
Demand forecasting is influenced by both internal factors and
external factors: external factors include competition, economic climate, laws
and regulatory bodies, changes in technology, and social factors whereas
internal factors are budget constraints, production level, new products and
services, organizational structure and employee separations.
Demand forecasting is essential because it helps the
organization to
1. Quantify the jobs, necessary for producing a given number of
goods,
2. To determine the nature of staff mix required in the future,
3. To
assess appropriate levels in different parts of the organization to avoid
unnecessary costs to the organization,
4. To prevent shortages of personnel
where and when they are needed by the organization.
5. To monitor compliances with legal
requirements about the reservation of jobs.
Techniques like managerial judgment, ratio-trend analysis,
regression analysis, work-study techniques, Delphi techniques are some of the
major methods used by the organization for demand forecasting.
HR Supply
Forecast:
The supply forecast determines whether the HR department will be
able to procure the required number of workers. Supply forecast measures the
number of people likely to be available from within and outside an
organization, after making allowance for absenteeism, internal movements and
promotions, wastage and changes in hours, and other conditions of work.
A supply forecast is required because it is needed as it 1.
Helps to quantify the number of people and positions expected to be available
in the future to help the organization realize its plans and meet its objectives 2.
Helps to clarify the staff mixes that will arise in the future 3. It assesses
existing staffing in different parts of the organization. 4. It will enable the organization to prevent a shortage
of people where and when they are most needed. 5. It also helps to monitor
future compliance with legal requirements of job reservations.
Supply analysis covers the existing human resources, internal
sources of supply, and external sources of supply.
HR
Programming:
Once an organization’s
personnel demand and supply are forecasted the demand and supply need to be
balanced so that the vacancies can be filled by the right employees at
the right time.
HR Plan
Implementation:
HR implementation requires converting an HR plan into action.
A series of actions are initiated as a part of HR plan implementation.
Programs such as recruitment, selection, and placement, training and
development, retraining and redeployment, retention plan, succession plan, etc
when clubbed together form the implementation part of the HR plan.
Control and
Evaluation:
Control and evaluation represent the final phase of the HRP
process. All HR plans include budgets, targets, and standards. The achievement of
the organization will be evaluated and monitored against the plan. During this
final phase organization will be evaluated on the number of people employed
against the established (both those who are in the post and those who are in
pipeline) and on the number recruited against the recruitment targets. Evaluation is also done concerning
employment costs against the budget and wastage accrued so that corrective
action can be taken in the future.